







Ziyi Wu1,3,
Daniel Watson1,
Andrea Tagliasacchi2,3,*,
David J. Fleet1,3,
Marcus A. Brubaker1,
Saurabh Saxena1,†
1Google DeepMind
2Simon Fraser University
3University of Toronto
* Work done at Google DeepMind
† Corresponding author
360Anything lifts arbitrary perspective images and videos to seamless, gravity-aligned 360° panoramas, without using any camera or 3D information. Our geometry-free DiT framework enables robust 360° novel view synthesis and 3D scene reconstruction from monocular videos.
We test our model on challenging conditioning videos with large object or camera motion. 360Anything is still able to infer the camera trajectory and generate stably canonicalized 360° panoramas.
Given a monocular video, naively fitting a 3DGS on it leads to broken results due to the low coverage of the scene. Instead, we first run 360Anything to synthesize the entire 360° view as a panorama video, and then train 3DGS on it. This leads to much better geometry and enables fly-through exploration of the 3D scene.
| Input Video | Outpainted Panorama Video | 3DGS on Input Video | 3DGS on Panorama Video (Ours) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
We show the input perspective videos, the text prompts, and the panorama videos generated by Imagine360 [1], Argus [2], ViewPoint [3], and our 360Anything. Red boxes highlight the area corresponding to the input video.
| Input | Imagine360 | Argus | ViewPoint | 360Anything (Ours) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caption: A person wearing a dark shirt and a hat holds the camera and is walking down a busy city street. | ||||
| Caption: A man in a dark grey t-shirt gestures towards a large green tank inside a dimly lit room. | ||||
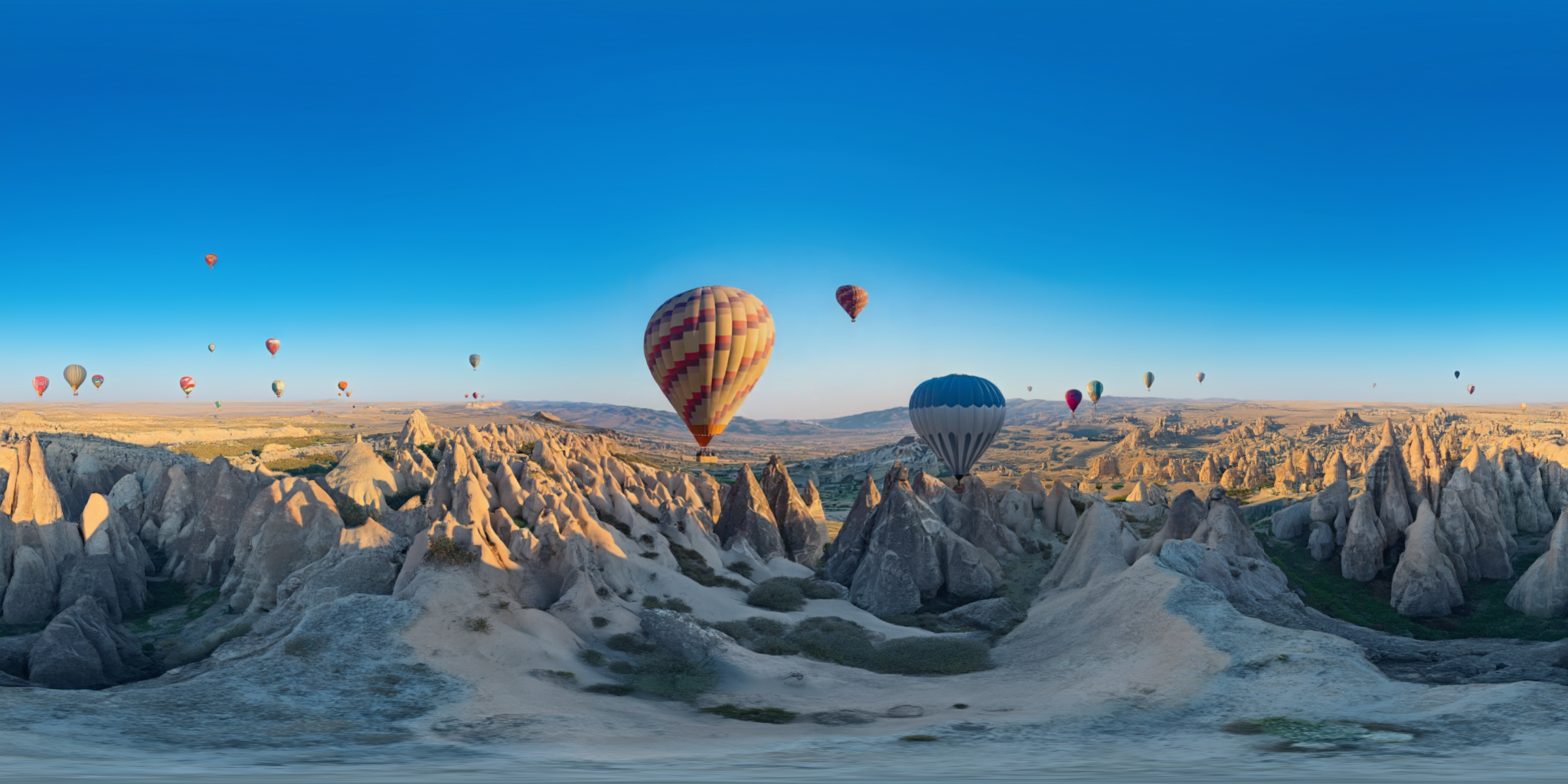
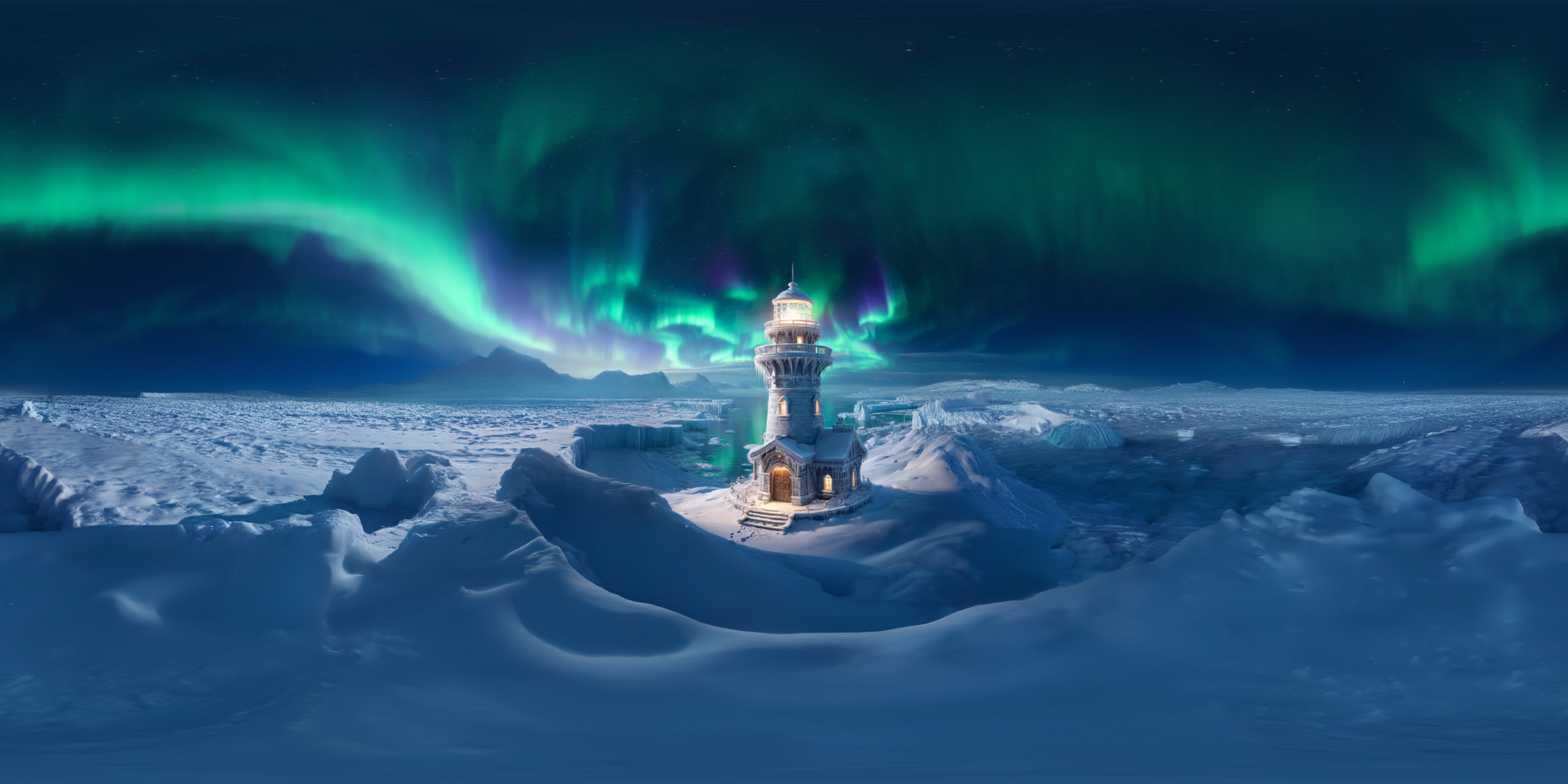
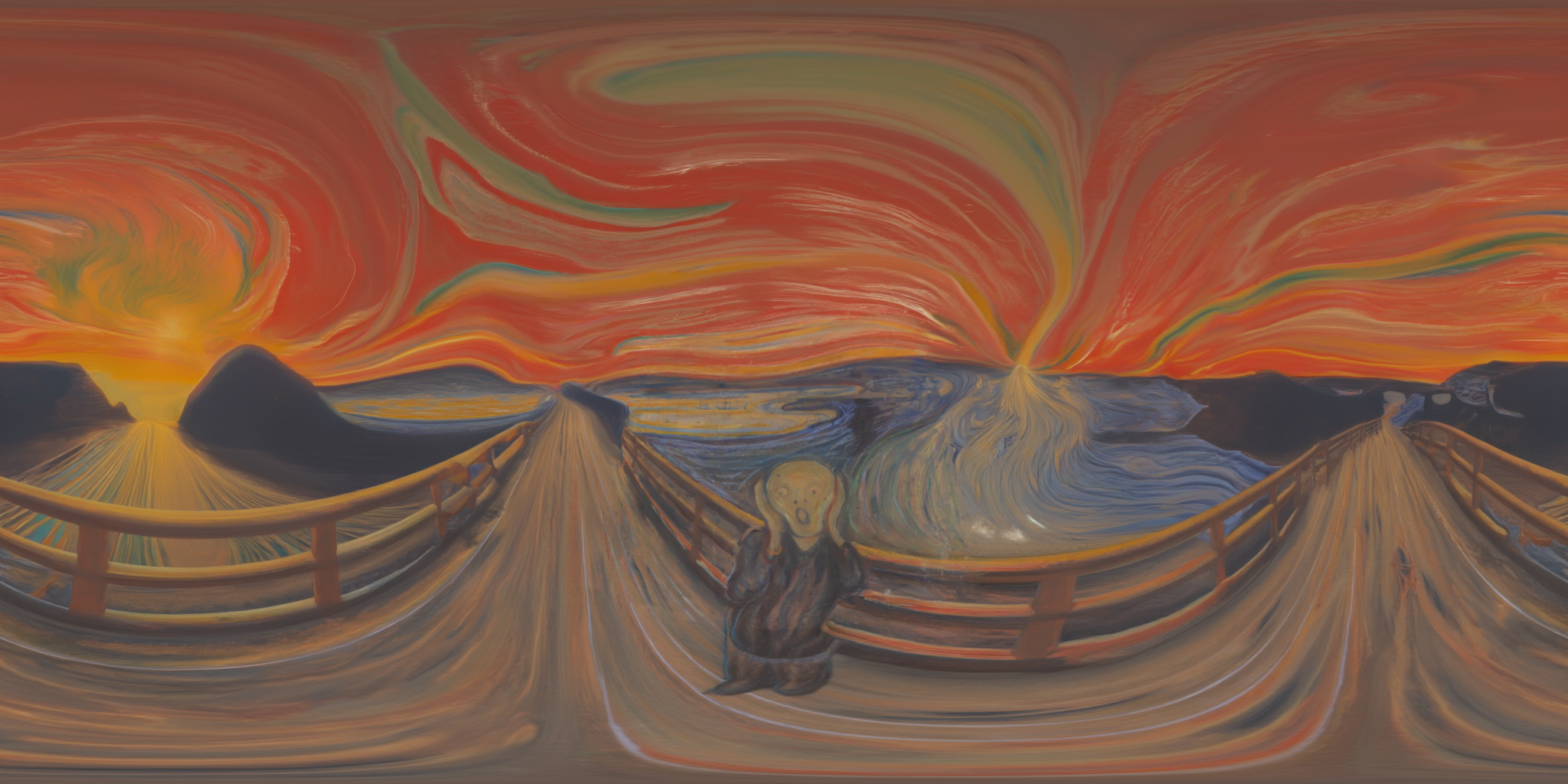
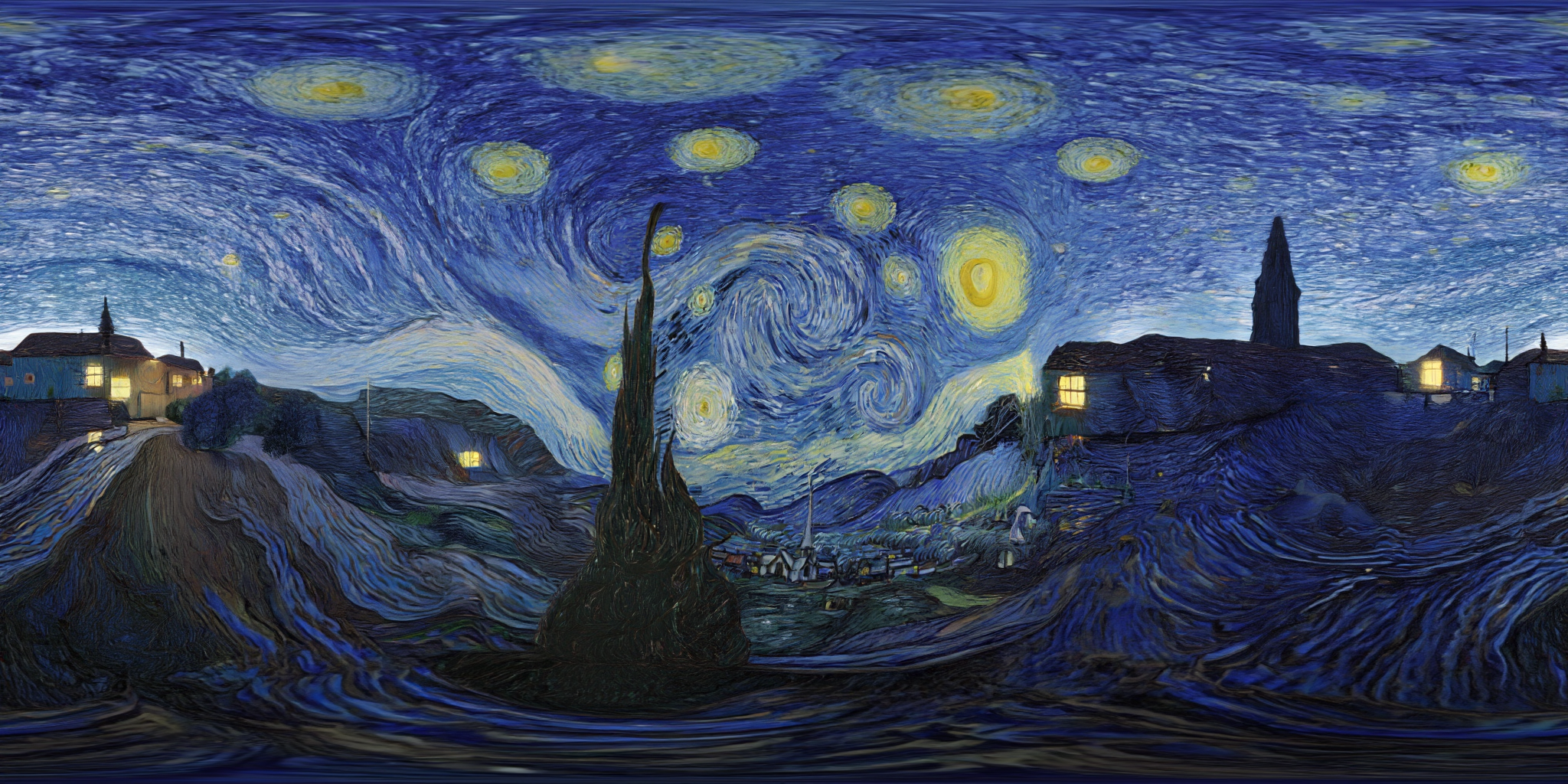
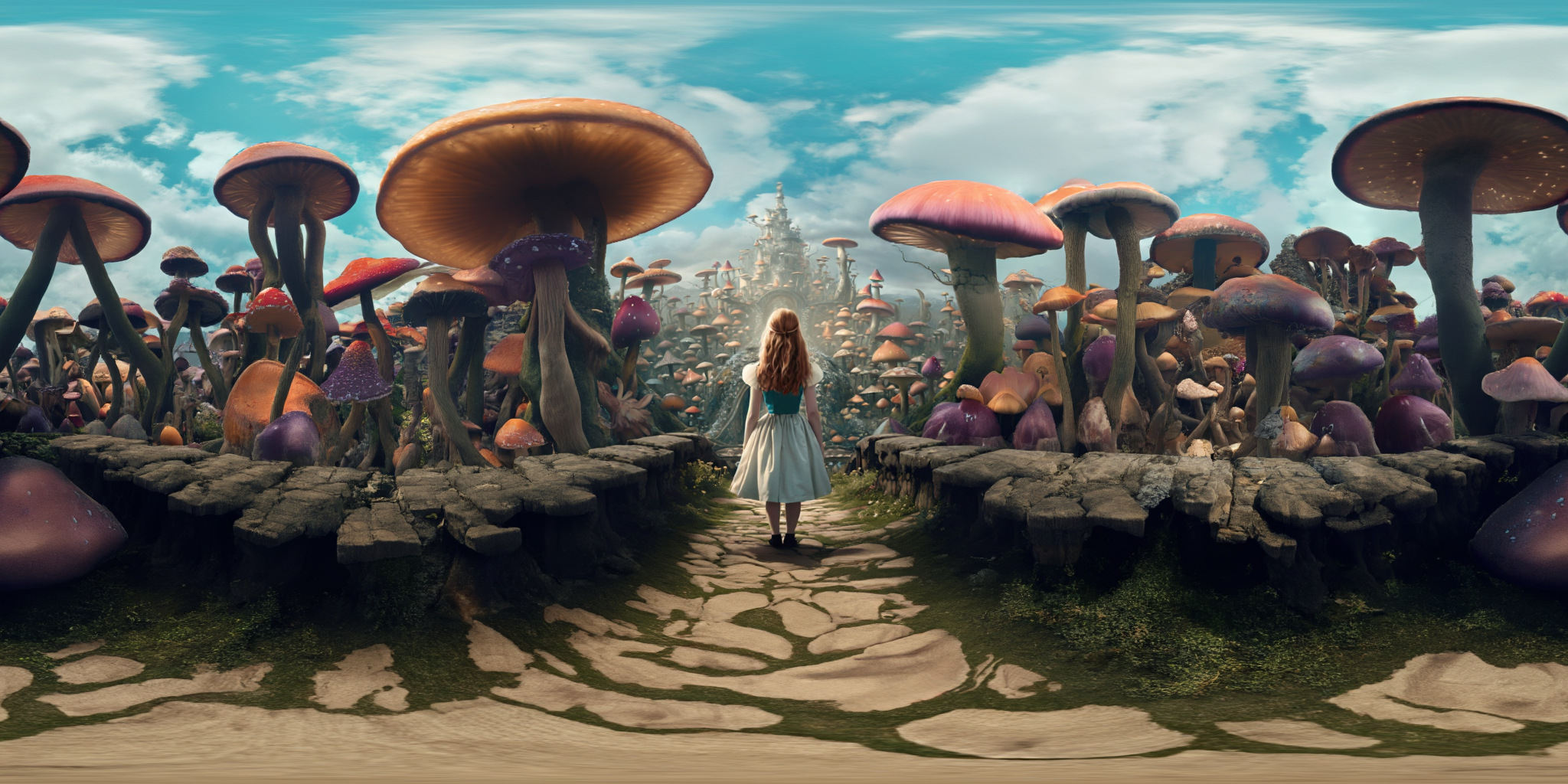
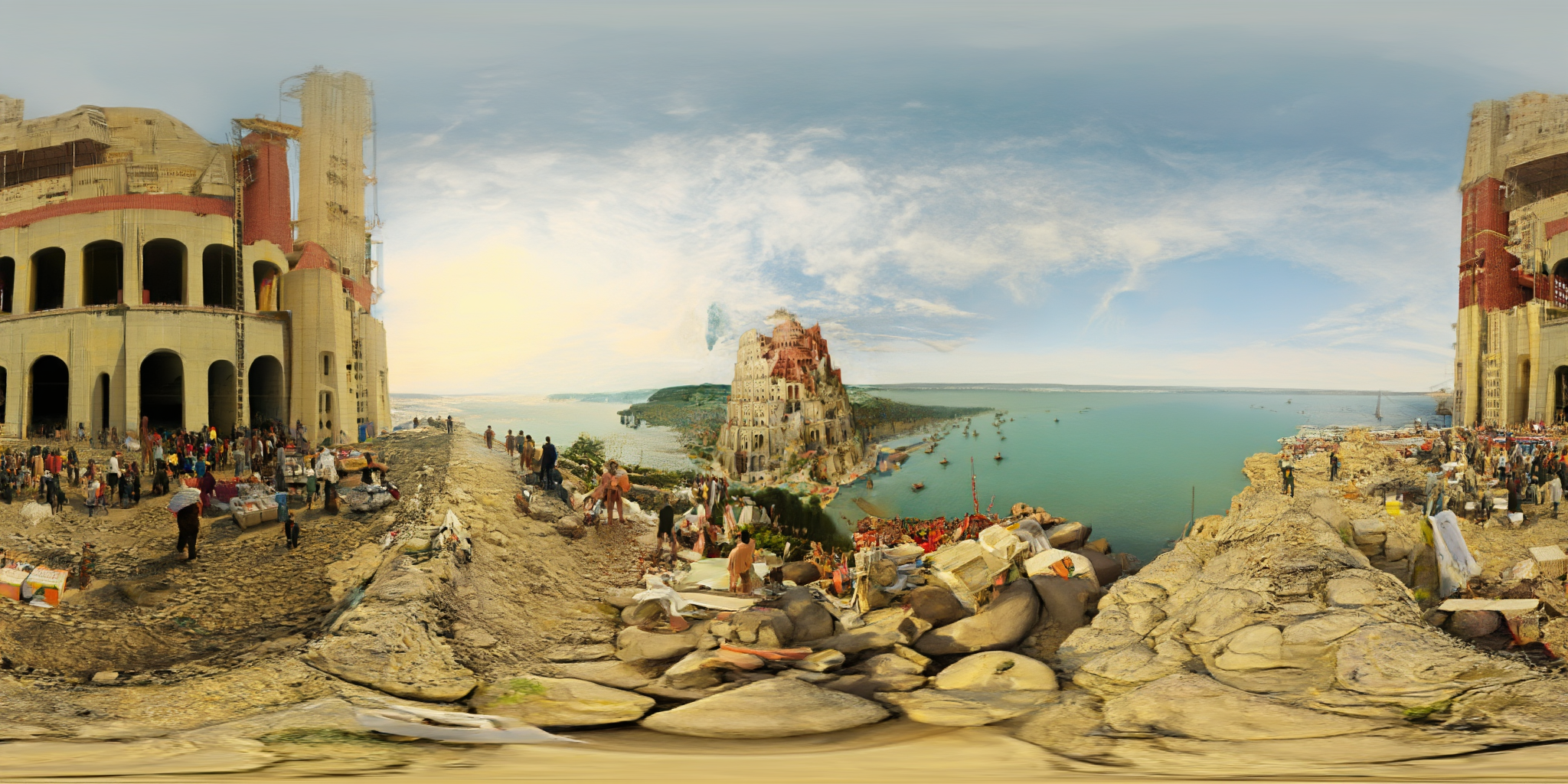
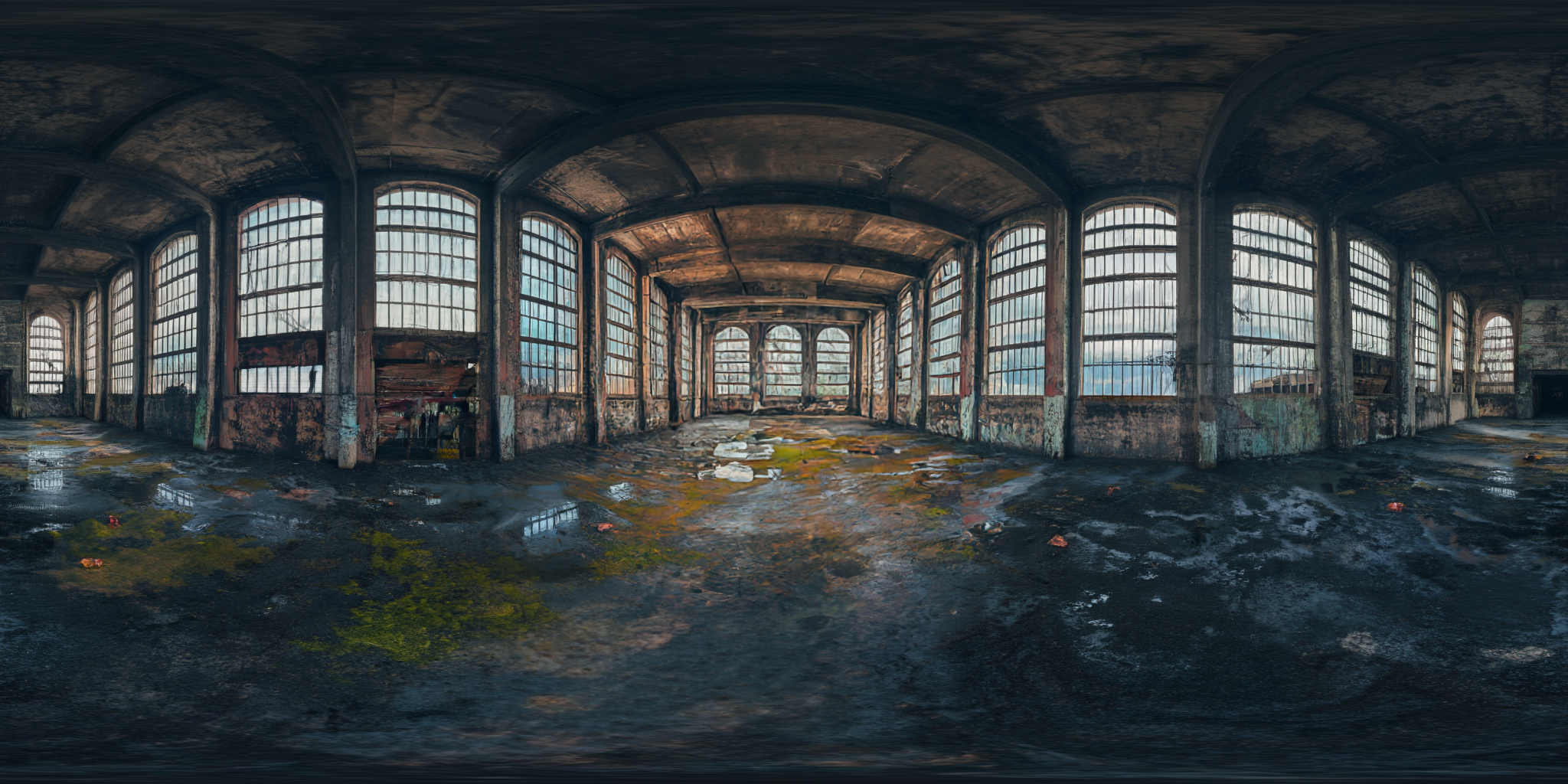
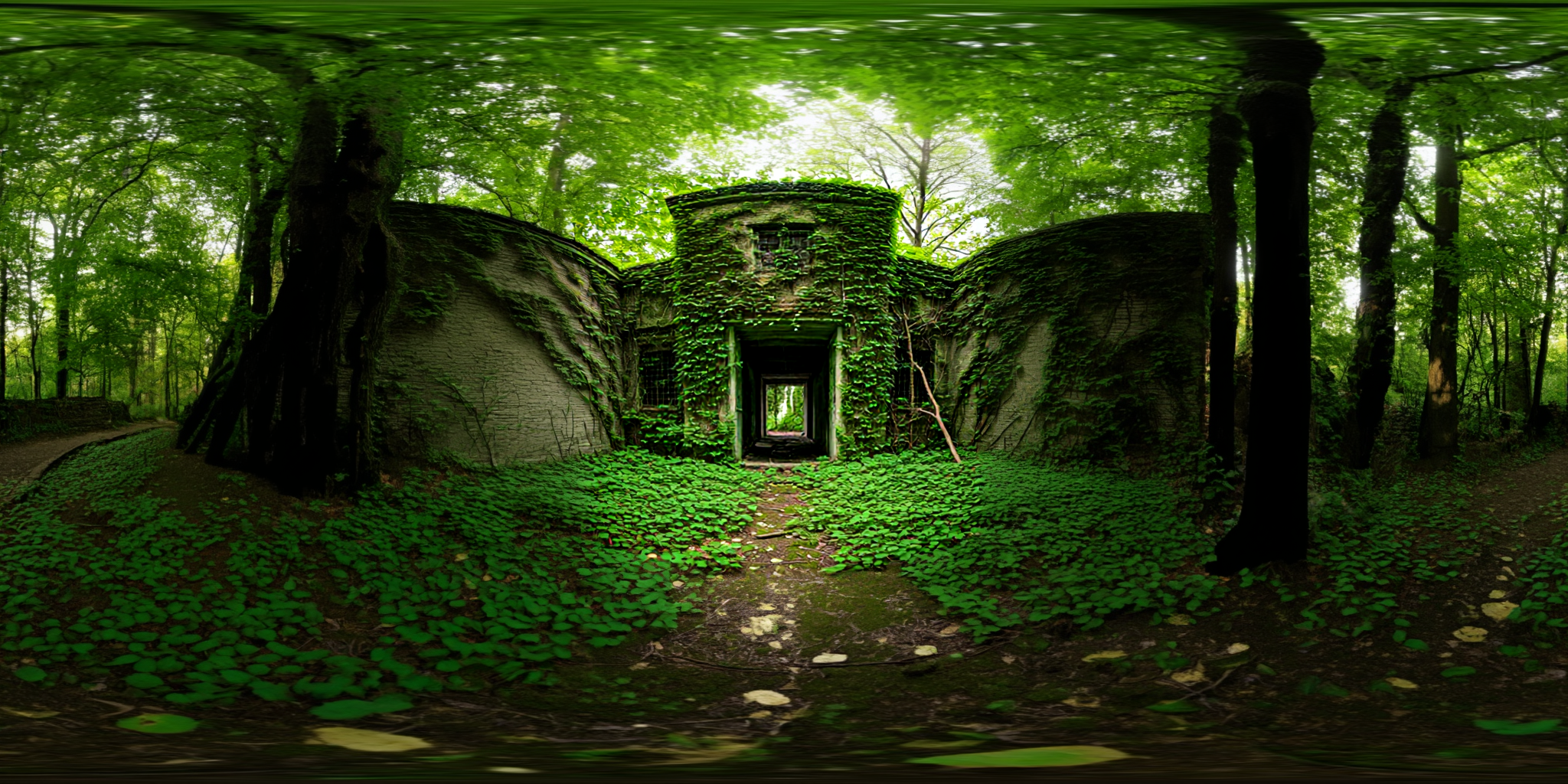
360Anything also applies to perspective-to-panorama image generation. We fine-tune FLUX on synthetic 360° rendering of 3D scenes, which generalizes to in-the-wild and OOD images.
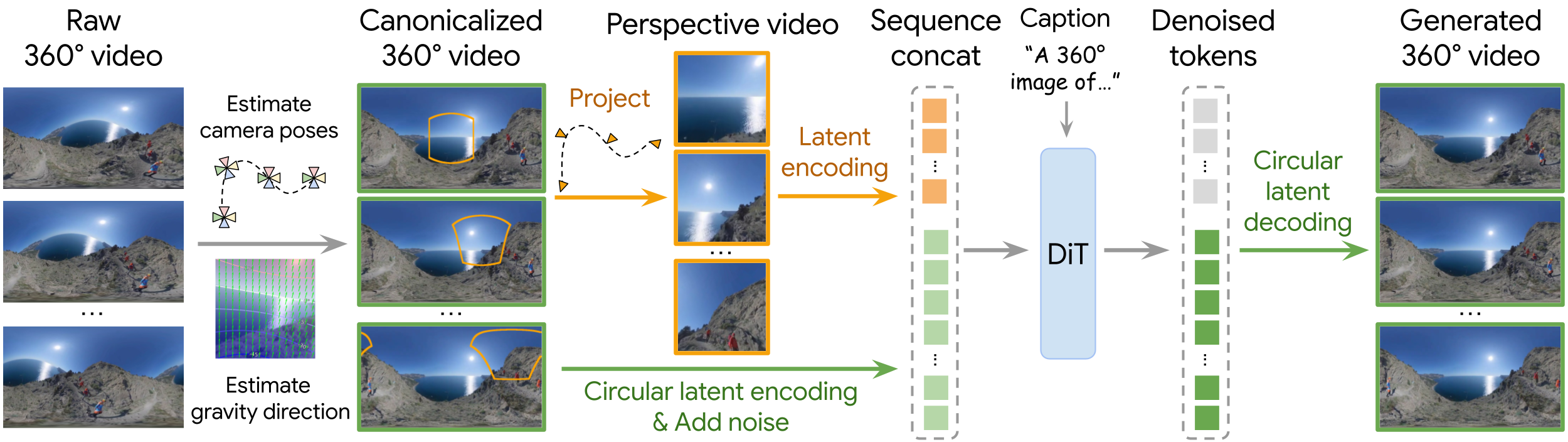
Given a raw 360° video with arbitrary camera orientations, we first follow a two-step canonicalization pipeline to make it a gravity-aligned (upright) 360° video. To train on such canonicalized data, we project the panorama video to perspective views with randomly sampled camera trajectories as model conditioning. We simply concatenate the conditioning tokens (orange) with the noisy latents of the target panorama (green) along the sequence dimension, and run a DiT for denoising. The model learns to infer the camera intrinsics and extrinsics from the data without any explicit supervision. We further desigh Circular Latent Encoding to eliminate the seam artifacts in the generated panoramas.
Since we do not provide explicit camera poses, the model can "place" the perspective input anywhere on the 360° canvas. We thus enforce the model to always generate panoramas in a gravity-aligned upright orientation, regardless of the camera pose of the perspective input. This requires canonicalizing all training panoramas, involving two steps:
| Raw | Stabilized | Canonicalized (Ours) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
@article{wu360anything,
title={{360Anything}: Geometry-Free Lifting of Images and Videos to 360°},
author={Wu, Ziyi and Watson, Daniel and Tagliasacchi, Andrea and Fleet, David J. and Brubaker, Marcus A. and Saxena, Saurabh},
journal={arXiv},
year={2026}
}
[1] Tan, Jing, et al. "Imagine360: Immersive 360 Video Generation from Perspective Anchor." NeurIPS. 2025.
[2] Luo, Rundong, et al. "Beyond the Frame: Generating 360° Panoramic Videos from Perspective Videos." ICCV. 2025.
[3] Fang, Zixun, et al. "Panoramic Video Generation with Pretrained Diffusion Models." NeurIPS. 2025.
[4] Kalischek, Nikolai, et al. "CubeDiff: Repurposing Diffusion-Based Image Models for Panorama Generation." ICLR. 2025.
[5] Wan, Team, et al. "Wan: Open and Advanced Large-Scale Video Generative Models." arXiv. 2025.
[6] Black Forest Labs. "FLUX." 2024.
We thank Nikolai Kalischek for help with the image data and Rundong Luo for help with the video data. We thank Noah Snavely and Richard Tucker for implementing the pipeline for running structure-from-motion at scale. We thank George Kopanas for help with the 3DGS experiments, Sara Sabour for discussion on 3D SfM, Lala Li for guidance on Gemini captioning, and Charles Herrmann and Jon Shlens for their feedback. We also thank the maxdiffusion contributors for converting FLUX and Wan from PyTorch to Jax. Some testing videos are from Veo, Genie 3, Sora, Gen4.5, and Wan; we thank them for sharing the videos.